Part:BBa_K3257003
lacIq Promoter
This part is lacIq promoter and it can be used to initiate the expression of lacI protein. In the lacIq allele, a single base change in the promoter boosts expression of the lacI gene about 10-fold.
Biology
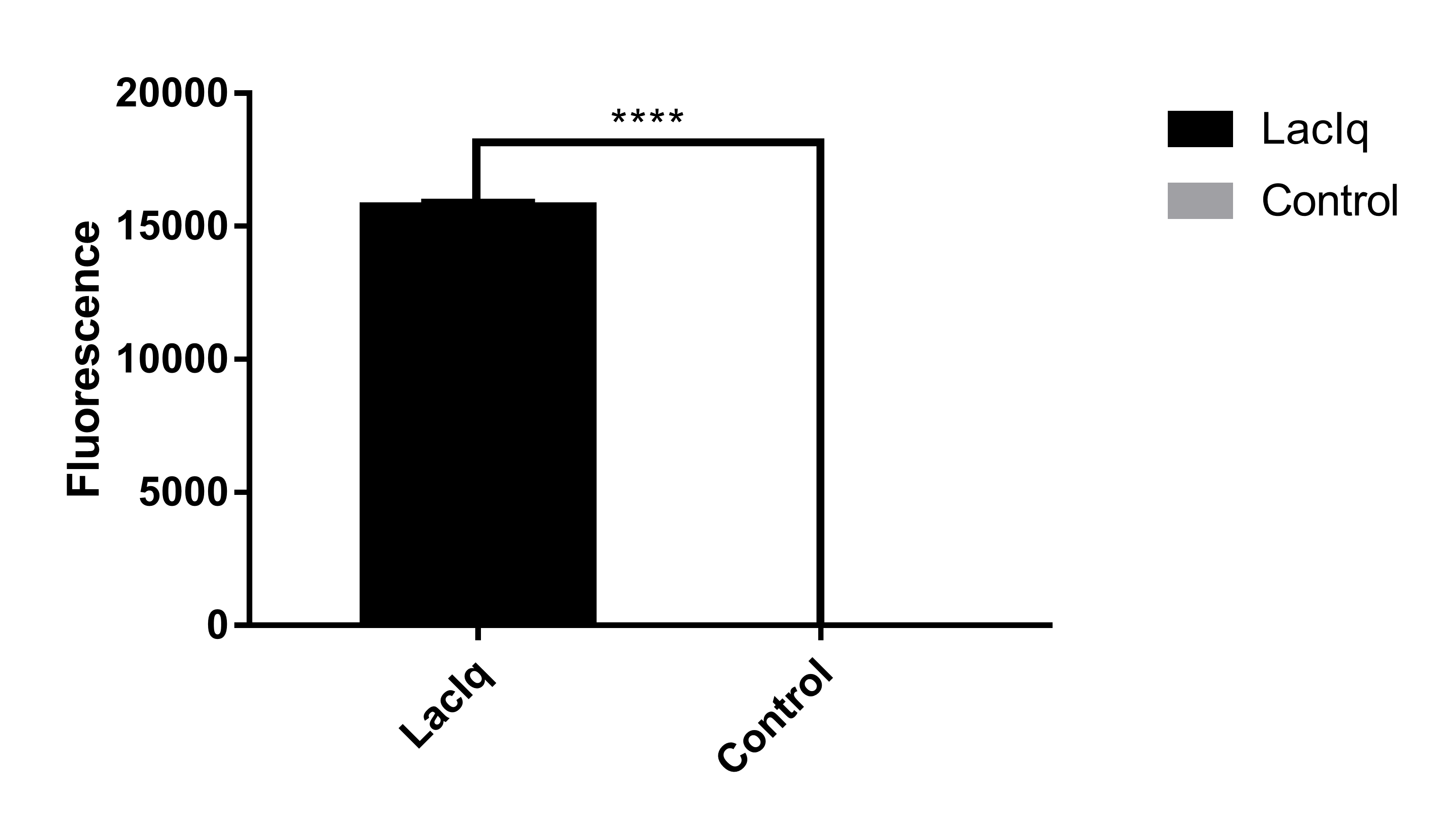
Contributed Information
Laciq Mutation Outcome:
The presence of the lacIq mutation leads to an elevated production of lac repressor compared to the wild-type strain.
The Iac repressor is a protein that stops the coding of proteins necessary for lactose metabolism. In E Coli, this lactose metabolism is necessary for survival should a more efficient sugar like glucose not be available.
LacIq Mutation Overview:
Characterised by a 15 base pair deletion within the lacIq promoter region.
A deletion is a mutation involving the loss of one (or more) nucleotides from a segment of DNA.
Interestingly, it replaces the suboptimal -35 region of the wild-type promoter with a sequence perfectly matching the consensus sequence for the six most crucial base pairs in the -35 region.
Transcriptional Impact of LacIq Mutation:
Facilitates an augmented transcription of I mRNA.
Leads to a subsequent increase in the quantity of lac repressor in lacIq strains.
Induction and Origin of LacIq Mutation:
LacIq mutation may have been induced by the usage of nitrosoguanidine, an alkylating agent that acts as a mutagen.
Alternatively, it may have emerged spontaneously during the selection process aimed at enhancing lacI expression.
Comparison with Wild-Type LacI Promoter:
Wild-type lacI promoter exhibits a relatively low level of transcription.
This is due to high levels of guanine-cytosine and the presence of a deficient -35 region that differs from other promoters.
Effect on Repressor Synthesis:
LacIq mutation results in a tenfold elevation in the level of repressor synthesis compared to the wild-type strain.
U J177 Mutation Impact:
U J177 mutation completely terminates the activity of the promoter.
Achieved by removing four base pairs, destroying the homology region at the -10 position.
Aoyama, T., Mituru Takanami, Eiko Ohtsuka, Yoshio Taniyama, Marumoto, R., Sato, H., & Ikehara, M. (1983). Essential structure ofE. colipromoter effect of spacer length between the two consensus sequences on promoter function. Nucleic Acids Research, 11(17), 5855–5864. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/11.17.5855
Calos, M. P., & Miller, J. H. (1981). The DNA sequence change resulting from the I Q1mutation, which greatly increases promoter strength. Molecular and General Genetics MGG, 183(3), 559–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00268783
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |
